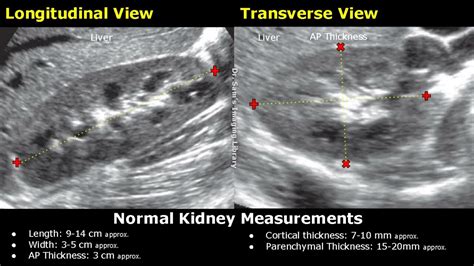
ultrasounds measure cortical thickness kidneys|kidney cortical thinning ultrasound images : purchase Measures of the kidney. L = length. P = parenchymal thickness. C = cortical thickness. Doppler examination of the kidney is widely used, and the vessels are easily depicted by the . Resultado da Acompanhantes e garotas de programa morenas em Taboão da Serra. Brasil. São Paulo. Taboão da Serra. Morenas. . Ferrary, bela garota de programa morena e uma gata da pele . Taboão da Serra 20 anos R$ 100. . bela e doce acompanhante carioca, morena simpática e linda por .
{plog:ftitle_list}
18:36. Sexta-Feira. 01/03/2024. Manhã 5% Tarde 88% Noite 5% Temperatura 34°. 21°. Índice UV 12. 06:04. 18:36. Obs: As horas apresentadas estão no horário de Brasília .
Our study suggests that ultrasonographic cortical thickness measurements may be an important imaging technique in the follow-up care of patients with CKD. Keywords: Renal . Measured in a longitudinal view from the kidney’s midpole boundary to the base of the medullary pyramids, cortical thickness is a common metric. The normal cortical thickness is 7-10 mm; reduced cortical thickness may indicate . The cortical thickness is measured from renal capsule to the base of the triangular medullary pyramids. The parenchymal thickness is measured from the renal .Longitudinal ultrasound image of right kidney shows cortical thickness measured perpendicularly from outer margin of kidney to corticomedullary junction (arrow). Measurement is 0.46 cm.
Measures of the kidney. L = length. P = parenchymal thickness. C = cortical thickness. Doppler examination of the kidney is widely used, and the vessels are easily depicted by the .The aim of this study was to assess the accuracy of crude and composite ultrasound parameters based on kidney measurements and cortical echogenicity to detect renal dysfunction and .
Ultrasound imaging is a key investigatory step in the evaluation of chronic kidney disease and kidney transplantation. It uses nonionizing radiation, is noninvasive, and generates real-time . Ultrasonography of the kidneys is essential in the diagnosis and management of kidney-related diseases. The kidneys are easily examined, and most pathological changes in the kidneys are distinguishable with .
laser coating thickness measurement
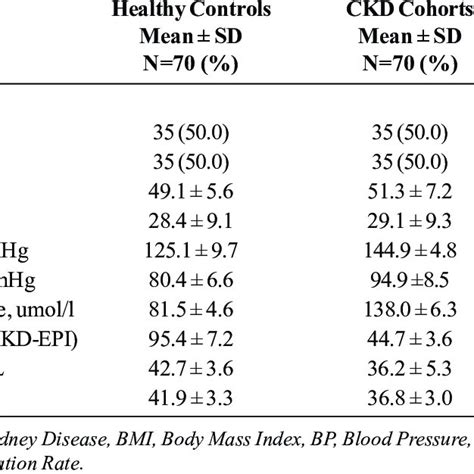
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of our study was to determine whether there is a relationship between renal cortical thickness or length measured on ultrasound and the degree of renal impairment in chronic kidney disease (CKD). MATERIALS AND METHODS. From October to December 2007, 25 patients (13 men and 12 women, mean age 73 years) were identified who had CKD .between renal cortical thickness or length measured on ultrasound and the degree of renal impairment in chronic kidney disease (CKD). MATERIALS AND METHODS. From October to December 2007, 25 patients (13 men and 12 women, mean age 73 years) were identified who had CKD but were not on di-alysis. 2.1. Study Population. This study included 137 patients who underwent abdominal ultrasonography between April 2014 and March 2015. Among them, patients with diabetes mellitus, unilateral kidney, renal tumor, hydronephrosis, solitary cyst greater than 4 cm in diameter, polycystic kidney disease, acute kidney injury defined by risk of renal dysfunction, . Causes of echogenic kidneys on ultrasound can include: acute and chronic kidney disease, sickle cell disease, kidney disease related to HIV, renal amyloidosis, and dehydration. Is echogenic kidney dangerous? It can be in some cases when the cause is related to kidney disease. More testing will be needed to be certain.
Ultrasound discovered the right kidney was sitting below the left kidney. It was rotated and the distal ureteric jet was on the right side. . Cortical thickness(not <10mm) Cortico-medullary differentiation; Cortex at least as hypoechoic as the liver; . Both kidneys with length measurements; Right kidney long with liver for comparison; Spiral CTA was performed in 49 hypertensive patients. Renal diameters, renal length, and cortical thickness were measured in 26 post-stenotic kidneys, 26 contralateral kidneys and 46 control kidneys. . The measurement of cortical thickness also revealed significant lesions in contralateral kidneys without stenosis. . Eur J Ultrasound. 1998 .There was a significant decline in creatinine clearance in subjects who were >60 years of age compared to those <30 years (100 vs. 135 ml/min, respectively, p < 0.005) but without a corresponding reduction in renal length (10.5 vs. 10.75 cm, respectively, p = 0.47; table 2).Similarly, the reduction of cortical thickness with age was not statistically significant (0.89 . Some nephrologists use the cortical thickness over the renal length measurement to determine the severity of renal failure as well as to follow the patient for progression of the disease. FIGURE 12-4 Image demonstrating how to measure cortical thickness (solid line . Some ultrasound (US) units can calculate the renal volume from the .
reduced renal cortical thickness <6 mm 6 more reliable than length 7. reduced renal length. increased renal cortical echogenicity poor visibility of the renal pyramids and the renal sinus. marginal irregularities. papillary calcifications. cysts (see also: acquired cystic kidney disease) Abnormal Doppler findings in these patients include 2:
The classic finding in renal artery stenosis is asymmetry between the kidneys, with a reduction in kidney size and cortical thickness on the side of the stenosis (Fig 10A and B) that is often accentuated by hypertrophy of the contralateral kidney (Fig 10B). . What is the value of measuring renal parenchymal thickness before renal biopsy? Clin .
sured at the middle third portion of the kidney. All measurements were obtained prospectively on static original ultrasound images using electronic calipers at the time of scanning. Renal length, parenchymal thickness, and med-ullary pyramid thickness measurements were per-formed for each kidney. Mean measurements were calculated for . Measuring the kidney’s cortical thickness can help detect kidney disease and assess the extent of renal function loss. Renal cortical thickness can be measured using ultrasound imaging techniques, including scanning the kidneys during a transabdominal ultrasound. This method is simple, non-invasive, and cost-effective. .The renal cortical thickness (RCT) reflects the pathological condition of the kidney, and measuring this parameter can help diagnose renal fibrosis in dogs. The normal reference range of RCT in dogs is broad (3-8 mm) because of the extreme diversity in body size. Therefore, this retrospective, refer .OBJECTIVE. The objective of our study was to develop, by use of ultrasound, nomograms of renal parenchymal thickness, medullary pyramid thickness (height), renal length, and the ratio of medullary pyramid thickness to .
Height-adjusted cortical thickness could predict renal dysfunction with the area under the curve of 0.786, and height-adjusted cortical thickness of 4.0 mm/cm was a cut off value with a sensitivity of 72.5% and a specificity of .
common metric. The normal cortical thickness is 7-10 mm; reduced cortical thickness may indicate progressive kidney disease or decreased eGFR.11,15,16 With respect to volume, the normal range in men is 110-190 mL and in women is 90-150 mL.17 It is possible to measure volume by simplifying the kidney’s shape as The adult kidney size is variable due to the correlation with body height and age; however, normograms for pediatric kidney size are available. Measure cortical thickness: Cortical thickness should be estimated from the base of the pyramid and is generally 7–10 mm. If the pyramids are difficult to differentiate, the parenchymal thickness can . Methods: Renal ultrasound (US) parameters including renal length, parenchymal thickness, cortical thickness and medullary thickness were assessed in 176 subjects, who were categorized into 4 groups based on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (ml/min/1.73 m 2): group 1, ≥90; group 2, ≥60 but <90; group 3, ≥30 but <60; and group 4 .
How reliable is renal ultrasound to measure renal length and volume in patients with chronic kidney disease compared with magnetic resonance imaging? . Machan JT, et al. Renal cortical thickness measured at ultrasound: is it better than renal length as an indicator of renal function in chronic kidney disease? Am J Roentgenol 2010; 195:W146 .
between renal cortical thickness or length measured on ultrasound and the degree of renal impairment in chronic kidney disease (CKD). MATERIALS AND METHODS. From October to December 2007, 25 patients (13 men and 12 women, mean age 73 years) were identified who had CKD but were not on di-alysis. The ultrasound measurements of kidneys between puppies and kittens showed a significant difference. . Conclusion: Ultrasonographic measurement of renal cortical thickness plays a vital role in .
The widely accepted normal ultrasonographic measurement for kidneys in a cat varies between 3 and 4.3 cm in length. One report proposed that feline kidneys can measure 3.2 to 4.1 cm in length, 2.2 to 2.8 cm in width, and 1.9 to 2.5 cm in height. 1 Currently, there is no widely accepted method for determining ultrasonographically normal kidney size for dogs. In adults, the medullary pyramids are often indistinct on ultrasound imaging making the measurement of cortical thickness inaccurate. Therefore, parenchymal thickness is often easier to measure. A renal parenchymal thickness under 1 cm is considered abnormal . Figure 5.9 demonstrates cortical versus parenchymal thickness measurements. Background Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is progressive, requiring constant monitoring to inform aggressive therapy that halts disease progression. Besides laboratory tests, ultrasound is safe, inexpensive, and ubiquitous, and can be used to monitor CKD patients non-invasively. Several studies have tried to correlate ultrasound parameters like renal bipolar .
Methods: Renal ultrasound (US) parameters including renal length, parenchymal thickness, cortical thickness and medullary thickness were assessed in 176 subjects, who were categorized into 4 .
The normal ultrasound appearances of the kidney vary with age. Initially, in the neonatal period, there is almost no medullary fat. . In both the neonatal and paediatric kidney, the foetal cortical lobulations are pronounced and should span the pyramids (as seen in the images below). . Obtain an accurate length measurement of each kidney .
renal cortical thickness normal range
Para acessar seu exame, digite o endereço no site para resultados de exames da FIDI (resultados.fidi.org.br) do seu computador, tablet ou celular. Perdi a data do meu exame, posso remarcar? Como o exame é realizado através de agendamento feito na própria Unidade de Saúde, deve o interessado procurar esta mesma Unidade e realizar novo .
ultrasounds measure cortical thickness kidneys|kidney cortical thinning ultrasound images